Using cells selected in the ABC Atlas with Gene Expression data.#
The Allen Brain Cell (ABC) Atlas is a powerfull tool for visualizing the data that are used throughout these notebooks. One particualar way users can interact with the ABC Atlas is by selecting and downloading specific cells from either a part of the taxonomy UMAP or brain region they are interested. This notebook will show how combine these cells selected from the ABC Atlas with gene expression data and metadata in these notebooks.
Note that the examples in this notebook can only be used with the Whole Mouse Brain (WMB) MERFISH and 10X data, the Zhuang et al. MERFISH data (1-4), and the Whole Human Brain (WHB) 10X data. The Seattle Alzheimer’s Disease (SEA-AD) dataset is not currently available through this repository (Data and documentation for SEA-AD are available here).
For this notebook, the user should:
Have some familiarity with using the ABC Atlas. If you are unsure of any steps used to manipulate data in the atlas visualization, you can refer to the user guide here.
Be using manifest versions equal to or greater than 20241115. Instructions on listing and changing versions can be found in the Getting Started notebook.
Be connected to the internet.
Have run through the Getting Started and other notebooks in this repo.
Initializing required modules and instantiating the AbcProjectCache.#
import anndata
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from pathlib import Path
from PIL import Image
from abc_atlas_access.abc_atlas_cache.abc_project_cache import AbcProjectCache
We will interact with the data using the AbcProjectCache. This cache object tracks which data has been downloaded and serves the path to the requsted data on disk. For metadata, the cache can also directly serve a up a Pandas Dataframe. See the getting_started notebook for more details on using the cache including installing it if it has not already been.
Change the download_base variable to where you have downloaded the data in your system.
download_base = Path('../../data/abc_atlas')
abc_cache = AbcProjectCache.from_cache_dir(download_base)
abc_cache.current_manifest
'releases/20250531/manifest.json'
Selecting Data in the ABC Atlas.#
For this example we’ll be looking at the WMB MERFISH dataset within ABC Atlas. We’ll filter the data by a specific subtype and region and then select cells from a specific MERFISH slice. You can refer to this linked view of the atlas to see the cells we will be selecting.
The cells we select come from the L5 ET CTX Glut subclass, we’ll also filter on only cells in the VISpm sub-region of the Isocortex. This initial selection leaves 325 cells that overlap with our filters. We’ll use the select tool (dashed box in the upper corner in the linked ABC Atlas view) to select the cells in section 31 of our MERFISH data. Refer to the image below to see our selection and where these selected cells reside (in addition to the above link).
image = Image.open('data/abc_atlas_selection_merfish.png')
image
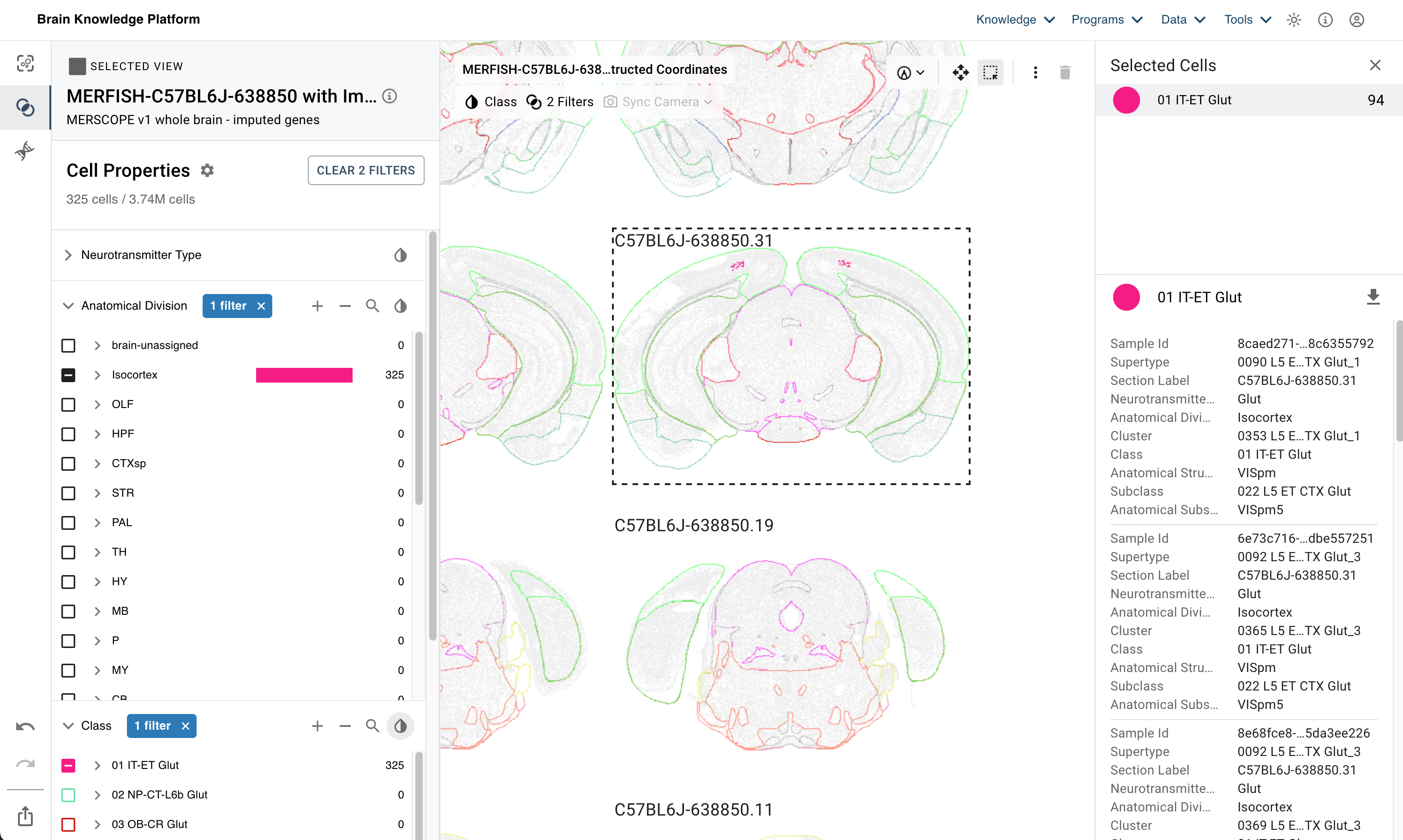
This gives us 94 cells in our final selection. We download the file by clicking the download arrow on the far right just above our listed, selected cells. This specific selection is provided in the file ABC_Atlas_Class_01 IT-ET Glut_cells_2024_10_23_16_42.csv that is packaged in this repo with the notebooks.
Combining with the cell metadata.#
Now that we have our subset of cells selected from the ABC Atlas, we can combine them with the cell metadata provided by the AbcProjectCache object.
The files cell_metadata in the projects/directories MERFISH-C57BL6J-638850, WHB-10Xv3, WMB-10X, Zhuang-ABCA-[1-4] contain a column abc_sample_id that allows for merging of data downloaded from an ABC Atlas visualization. Note that only the specific files called cell_metadata contain this id. Other derived metadata such as cell_metadata_with_cluster_annotation do not contain this id though it can be easily merged in.
Here we’ll just display a few columns of the cell_metadata table. For specifics on the MERFISH metadata and gene expression data used in this example, see the notebooks related this MERFISH dataset
cell_metadata = abc_cache.get_metadata_dataframe(
directory='MERFISH-C57BL6J-638850',
file_name='cell_metadata',
dtype={"cell_label": str},
)
cell_metadata.set_index('cell_label', inplace=True)
cell_metadata.head()[['brain_section_label', 'abc_sample_id']]
| brain_section_label | abc_sample_id | |
|---|---|---|
| cell_label | ||
| 1019171907102340387-1 | C57BL6J-638850.37 | c9881423-76a7-4835-ba8b-7942fd384b6b |
| 1104095349101460194-1 | C57BL6J-638850.26 | aa815488-6487-4e47-8a5e-d82ac9933bc6 |
| 1017092617101450577 | C57BL6J-638850.25 | 91ef7a85-8e3e-4410-8ee2-785788df3ebe |
| 1018093344101130233 | C57BL6J-638850.13 | 18991e17-fbd3-4ba0-9c60-1281f56ac520 |
| 1019171912201610094 | C57BL6J-638850.27 | 5e155936-e40d-4c6b-8971-e7fb0079274b |
Now we load our selected cells. Note that we rename the Sample Id column to match the one in our cell metadata.
# Change path location below to either your own downloaded cells
# or the location of the csv from this repo (abc_atlas_access/notebooks/ABC_Atlas_Class_01 IT-ET Glut_cells_2024_10_23_16_42.csv)
downloaded_cells_path = Path('data/ABC_Atlas_Class_01 IT-ET Glut_cells_2024_10_23_16_42.csv')
abc_atlas_selection = pd.read_csv(downloaded_cells_path)
abc_atlas_selection.rename(
columns={'Sample Id': 'abc_sample_id'},
inplace=True
)
abc_atlas_selection.set_index('abc_sample_id', inplace=True)
abc_atlas_selection.head()
| Supertype | Section Label | Neurotransmitter Type | Anatomical Division | Cluster | Class | Anatomical Structure | Subclass | Anatomical Substructure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abc_sample_id | |||||||||
| e23109f2-b70b-48a0-b29f-f4cfd24025ac | 0090 L5 ET CTX Glut_1 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0352 L5 ET CTX Glut_1 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| d42c7e04-95f7-4134-93e8-66acc1a52aa3 | 0091 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0359 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| cfc13cd0-adf7-41c4-a849-f1472ea31567 | 0091 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0359 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| e98716b6-15c2-4f54-8717-589b0da6d246 | 0090 L5 ET CTX Glut_1 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0352 L5 ET CTX Glut_1 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| a28ebb39-2849-49ae-80e4-ee135fce1890 | 0092 L5 ET CTX Glut_3 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0369 L5 ET CTX Glut_3 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
Now we can use pandas functionality to inner join together to two tables, leaving only the subset of cells, 94, that we selected in the ABC Atlas visualization.
selected_cells = cell_metadata.join(abc_atlas_selection, on='abc_sample_id', how='inner')
print(len(selected_cells))
selected_cells.head()
94
| brain_section_label | cluster_alias | average_correlation_score | feature_matrix_label | donor_label | donor_genotype | donor_sex | x | y | z | abc_sample_id | Supertype | Section Label | Neurotransmitter Type | Anatomical Division | Cluster | Class | Anatomical Structure | Subclass | Anatomical Substructure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cell_label | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1018093345102260085 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | 384 | 0.651028 | C57BL6J-638850 | C57BL6J-638850 | wt/wt | M | 4.087788 | 3.208372 | 5.4 | 21c31354-1979-4b93-b6f2-acaefaa22842 | 0091 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0360 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| 1018093345101290596 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | 384 | 0.737842 | C57BL6J-638850 | C57BL6J-638850 | wt/wt | M | 6.753508 | 3.045020 | 5.4 | 484abbf0-56d4-4622-add2-24920cd3cd05 | 0091 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0360 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| 1018093345102270314 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | 393 | 0.685347 | C57BL6J-638850 | C57BL6J-638850 | wt/wt | M | 3.936859 | 3.295320 | 5.4 | 147ac3d0-b2f2-4e1c-bd00-e1b740b242bc | 0091 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0364 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| 1018093345102260156 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | 383 | 0.808770 | C57BL6J-638850 | C57BL6J-638850 | wt/wt | M | 4.042362 | 3.188116 | 5.4 | eaf8a6aa-2ccd-474b-ac40-5bcbc705e2eb | 0091 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0359 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
| 1018093345101290474 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | 383 | 0.536743 | C57BL6J-638850 | C57BL6J-638850 | wt/wt | M | 6.833381 | 2.998880 | 5.4 | e4874d7b-6754-40ff-8792-c0b7627f2bce | 0091 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | C57BL6J-638850.31 | Glut | Isocortex | 0359 L5 ET CTX Glut_2 | 01 IT-ET Glut | VISpm | 022 L5 ET CTX Glut | VISpm5 |
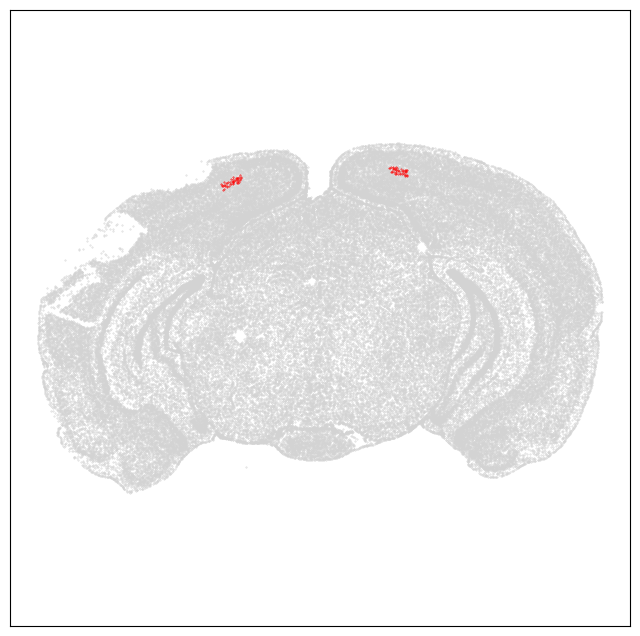
Let’s do a quick plot to show that we can grossly reproduces the view of MERFISH section 31.
def plot_section(xx, yy, cc = None, val = None, fig_width = 8, fig_height = 8, cmap = None, fig=None, ax=None):
if fig is None or ax is None:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(fig_width, fig_height)
if cmap is not None:
plt.scatter(xx, yy, s=0.5, c=val, marker='.', cmap=cmap)
elif cc is not None:
plt.scatter(xx, yy, s=0.5, color=cc, marker='.')
ax.set_ylim(11, 0)
ax.set_xlim(0, 11)
ax.axis('equal')
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
return fig, ax
pred = (cell_metadata['brain_section_label'] == 'C57BL6J-638850.31')
section = cell_metadata[pred]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(8, 8)
# Plot all cells as grey.
fig_all, ax_all = plot_section(section['x'], section['y'], cc='#D3D3D3', fig=fig, ax=ax)
# Plot our selected cells as red
fig_sel, ax_sel = plot_section(selected_cells['x'], selected_cells['y'], cc='red', fig=fig, ax=ax)
plt.show()
Using the matched data in a cell by gene matrix.#
Now that we have have our matched metadata we can simply use the index of our final combined Pandas DataFrame with our cell by gene data. Since we are working with data from an individual MERFISH slice, we can download that directly. If you are doing this with the 10X data, you should use the get_gene_data function tutorialized in the general_accessing_10x_snRNASeq_tutorial notebook.
First we need to load our gene list giving a mapping from identifier to symbol.
gene = abc_cache.get_metadata_dataframe(directory='MERFISH-C57BL6J-638850', file_name='gene').set_index('gene_identifier')
gene.head()
| gene_symbol | transcript_identifier | name | mapped_ncbi_identifier | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gene_identifier | ||||
| ENSMUSG00000026778 | Prkcq | ENSMUST00000028118 | protein kinase C, theta | NCBIGene:18761 |
| ENSMUSG00000026837 | Col5a1 | ENSMUST00000028280 | collagen, type V, alpha 1 | NCBIGene:12831 |
| ENSMUSG00000001985 | Grik3 | ENSMUST00000030676 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 3 | NCBIGene:14807 |
| ENSMUSG00000039323 | Igfbp2 | ENSMUST00000047328 | insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 | NCBIGene:16008 |
| ENSMUSG00000048387 | Osr1 | ENSMUST00000057021 | odd-skipped related transcription factor 1 | NCBIGene:23967 |
Now we’ll load and process the data. Selecting by cell id in our data files (even for large ones) is mostly safe on machines with smaller memory footprints. This is assuming one uses the backed option and doesn’t attempt to load too many cells (<1000 say). For larger files, the user will want to be carefulas most of the anndata files we release cannot be loaded into memory on a smaller scale computer. For an example of doing this, or loading across 10X that has been divided into multiple files, see the General Accesing 10X data notebook
# Load the anndata, cell by gene matrix.
file_path = abc_cache.get_file_path(
directory='MERFISH-C57BL6J-638850-sections',
file_name='C57BL6J-638850.31/log2'
)
adata = anndata.read_h5ad(file_path, backed='r')
# Create a landing Pandas DataFrame for the data.
selected_cell_gene_data = pd.DataFrame(index=selected_cells.index,
columns=adata.var.index)
# Find the subset of cells we selected in the full matrix.
mask = adata.obs.index.isin(selected_cells.index)
# Fill our DataFrame with the
selected_cell_gene_data.loc[selected_cells.index, adata.var.index] = adata.X[mask].toarray()
selected_cell_gene_data.columns = gene.gene_symbol
C57BL6J-638850.31-log2.h5ad: 100%|██████████| 190M/190M [00:23<00:00, 8.20MMB/s]
selected_cell_gene_data
| gene_symbol | Prkcq | Col5a1 | Grik3 | Igfbp2 | Osr1 | Syt6 | Cntnap3 | Lmo3 | Ntn1 | Otp | ... | Blank-16 | Blank-32 | Blank-18 | Blank-4 | Blank-28 | Blank-33 | Blank-34 | Blank-45 | Blank-23 | Blank-48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cell_label | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1018093345102260085 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.900271 | 1.847696 | 0.0 | 0.900271 | 0.0 | 0.900271 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345101290596 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.498822 | 0.685901 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.148877 | 1.780236 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345102270314 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.429679 | 1.429679 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345102260156 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.150413 | 1.907521 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.755238 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.755238 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345101290474 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.591793 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.591793 | 1.591793 | 0.0 | 1.591793 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 1018093345102270545 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.663865 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.663865 | 0.0 | 1.116793 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.663865 | 0.0 | 1.116793 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345102270307 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.264144 | 2.094565 | 0.0 | 0.553146 | 0.0 | 0.952008 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345102270242 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.782628 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.782628 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345101290541 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.866036 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.403429 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.866036 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 1018093345101290626 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.860291 | 0.0 | 1.626302 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.626302 | 1.257898 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.761911 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
94 rows × 550 columns
This process can be repeated for the all other ABC Atlas visualizations (except SEA-AD which we do not currently released through this package). Here is a list of datasets in the AbcProjectCache that contain the abc_sample_id with links to their Abc Atlas bisualizations:
