Pulse Average (PA) plot¶
The purpose of the pulse averaging (PA) plot is to identify synaptic connections by pooling (via time alignment) and averaging the responses within and across sweeps to pulses (intended to produce action potentials) on a single headstage. It repeats this process for all headstages with pulses (action potentials).
Although the stimulus set will contain Pulse Train epochs in most cases, the pulse extraction algorithm works with all epoch types and special measurement modes like Distributed DAQ (dDAQ) or Optimized overlap distributed DAQ (oodDAQ).
The dDAQ slider from the Settings tab is respected as is the Channel Selection.
For instructional purposes, assume pulse train acquisition on four different headstages with oodDAQ (to distribute the pulses in time, across headstages). The PA plot shows AD data from each headstage and will have 16 (4 rows x 4 columns) PA sets (either in 16 plots on a single graph or 16 individual graphs; user-defined).
The diagonal entries hold the extracted single pulses for each headstage. In the other rows of each column are the regions plotted which are extracted from the other headstages at the same time coordinates as the diagonal pulses. So each row shows different regions from the same headstages, and each column shows the same region but from different headstages.
The following two figures, Trace plot and Image plot, were created with multiple sweeps overlayed, see Overlay Sweeps, and time alignment and zeroing turned on.
Trace plot¶
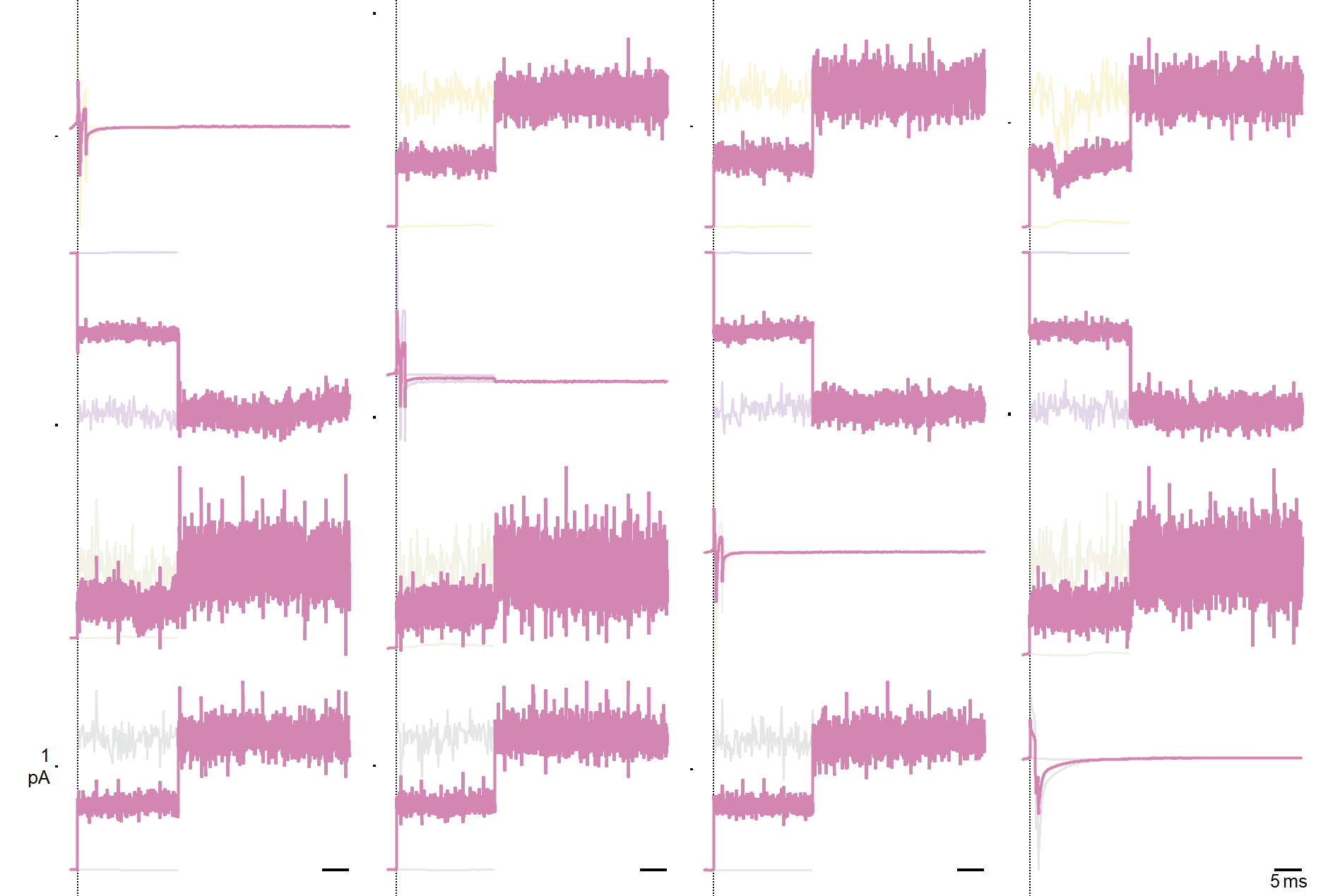
Trace plot¶
The trace plot displays data in each PA set as voltage or current time-series. Scale bars, shown in black, are provided for each y axes and for each column’s shared x (time) axes. PA trace colors match databrowser trace colors and encode the headstage, see also Relevant Colors.
Image plot¶
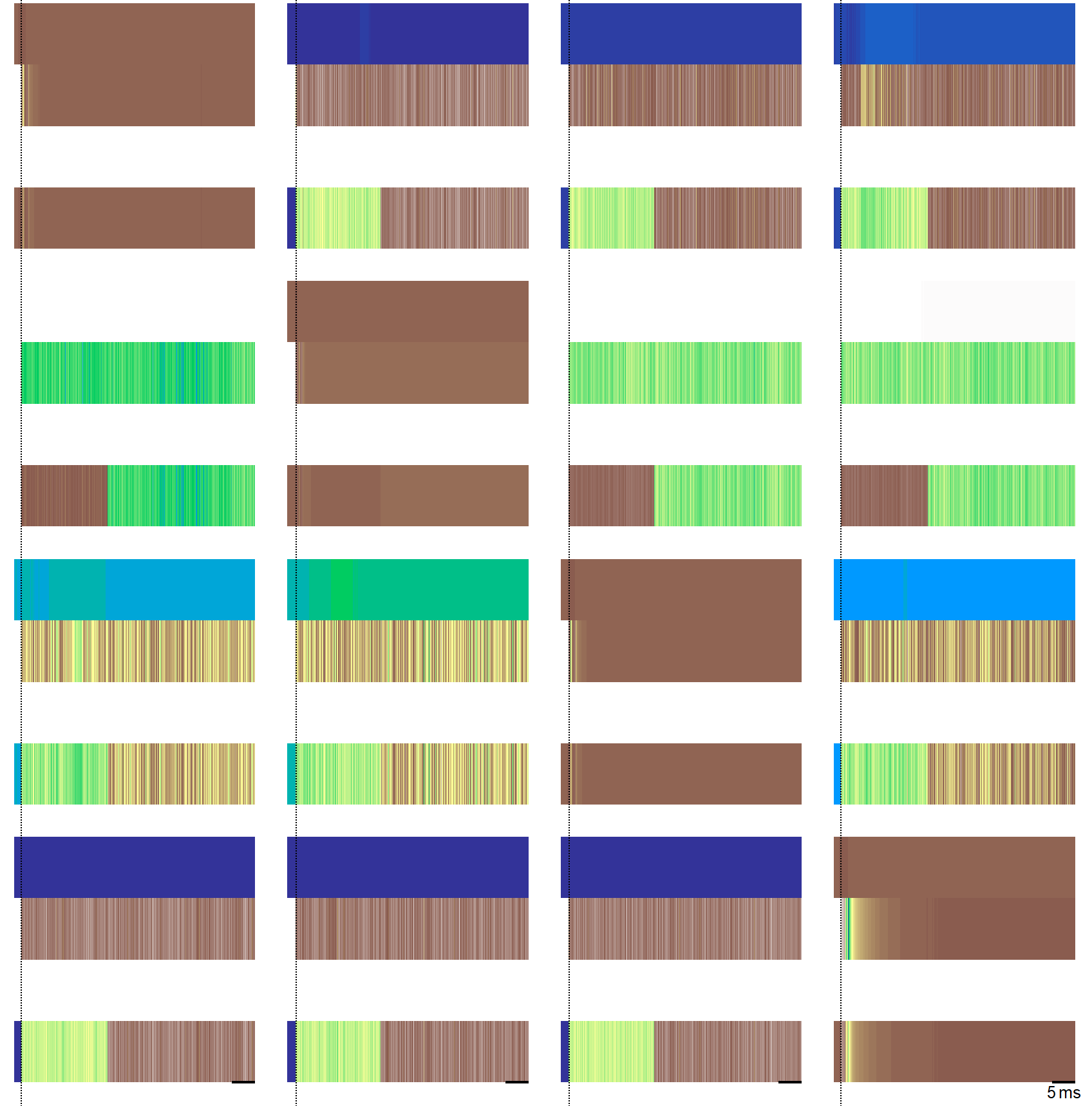
The image graph supplements the trace plot Trace plot. It renders more quickly than the trace plot, especially with many (overlayed) sweeps. Each (horizontal) line of the image plot corresponds to a pulse (unique time-series) and encodes the voltage or current in color (user-defined color mapping). Deconvolution and average lines (extra wide) are at the bottom of each set image. Image-space is left blank when data is not shown. The image is filled from top to bottom where the interleaving between pulses and sweeps depends on the Sort Order.
Sort Order¶
The following tables visualizes the display of one image set with two sweeps
overlayed and three pulses using different Sort Order settings. The
ordering is always ascending and from top to bottom. Due to implementation
details the Sweep sort order allows much faster incremental updates
(only relevant during data acqisition).
Sweep |
Pulse |
|---|---|
Pulse 0, Sweep 0 |
Pulse 0, Sweep 0 |
Pulse 1, Sweep 0 |
Pulse 0, Sweep 1 |
Pulse 2, Sweep 0 |
Pulse 1, Sweep 1 |
Pulse 0, Sweep 1 |
Pulse 1, Sweep 0 |
Pulse 1, Sweep 1 |
Pulse 2, Sweep 1 |
Pulse 2, Sweep 1 |
Pulse 2, Sweep 0 |
Average |
Average |
Deconvolution |
Deconvolution |
Time Alignment¶
Time alignment removes the pulse to pulse jitter in pulse evoked event (action potential) timing.
The algorithm is as follows:
Get the feature position
featurePos(wave maximum) for all pulses which belong to the same set. Store these feature positions using their sweep number and pulse index as key.Now shift all pulses in all sets from the same region by
-featurePoswherefeaturePosis used from the same sweep and pulse index.
Operation order¶
Data operations occur in the following (fixed) order:
Gather pulses
Pulse sorting
Failed pulse search
Zeroing
Time alignment
Averaging
PA plot settings¶
The following sections describe PA settings. Settings are configured on the data browser PA settings tab (shown below).
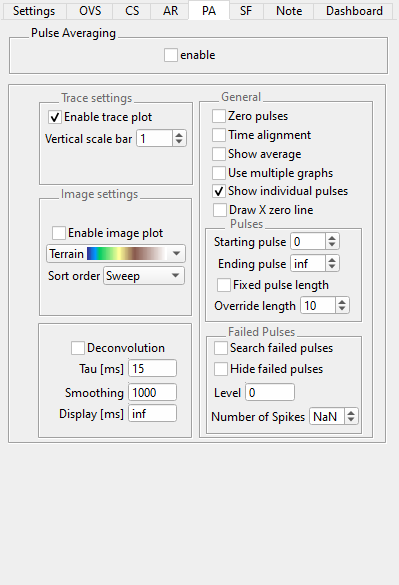
Settings for the pulse average plot¶
Pulse Averaging¶
enable: Toggle the display of the PA image/trace plots.To adjust multiple settings at-a-time, disable the PA plot, adjust settings, and re-enable.
Image settings¶
Enable image plot: Toggle the display of the Image plotDraw X zero line: Draws vertical line atX == 0in each column. Requires time alignment(see below). Facilitates measurement of event latency.
Popup Menu: Color scheme for image plotsSort order: Sort order of the displayed pulses. ForSweepthe pulses are first ordered by sweep number and then by pulse index. ForPulseit is first pulse index and then sweep number. See also Sort Order.
Trace settings¶
Enable trace plot: Toggle the display of the Trace plot.Vertical scale bar: Size of the vertical scale bar in y-axis units
Deconvolution¶
Deconvolution: Enables deconvolution [4] of the average pulse. Deconvolution trace is displayed with the average trace in the trace plot and immediately above the average line in the image plot.Tau [ms]: Time constant [5]Smoothing: Smoothing parameter, use1to disable smoothingDisplay [ms]: Time range of the average pulse used for the deconvolution, useinfto use the full range
General¶
Zero pulse: Toggle Pulse Zeroing. Zeroing is carried out by differentiation, followed by the integration of each pulse.Time alignment: Toggle time alignment of pulses from one column. See Time Alignment for an in-depth explanation.Show average: Toggle average pulse display. For the image plot, the average is the bottom-most row. Failed pulses (see below) are not included in the average.Use multiple graphs: Creates a panel for each PA set. Normally, multiple PA sets are distributed onto a single panel.Show individual pulses: Enables the display of individual pulses. Turning that off can increase the display update performance. The average and deconvolution are still shown if enabled.
Pulses¶
Select a subset of the pulses from a train of pulses (contained within a sweep).
Starting pulse: First pulse index to display, 0-based.Ending pulse: Last pulse index to display, useinfto use the last pulse.Fixed pulse length: Choose the calculation method of the pulse lengths. When unchecked the pulse length is calculated as the average pulse length from the extracted pulses. When checked theOverride lengthis used.Override length: Pulse length to use when no length can be calculated [6] or whenFixed pulse lengthis checked
Failed Pulses¶
Pulse responses may be filtered by their amplitude.
Search failed pulses: Toggle the failed pulse searchHide failed pulses: When a pulse failed, hide instead of highlight.Level: Level in y-data units to search for failed pulses. Every pulse not reaching that level is considered failing. As mentioned in Operation order that search is done before zeroing.Number of Spikes: Number of required spikes for each pulse. UseNaNfor accepting any non-zero spike count as passing.
Pulse length cannot be calculated when a sweep contains a single pulse
or when the pulse length is variable, e.g., Poisson distribution from the
Pulse Train stimulus epoch type.